Grapes are a popular fruit, known for their delicious taste and versatility in culinary uses, from fresh eating to winemaking. If you’re considering growing grapes, one of the first questions you might have is how long it takes for them to grow. The journey from planting to harvesting can vary depending on several factors, including the grape variety, climate, and growing conditions. Understanding this timeline is crucial for planning and ensuring a successful grape-growing venture. “How long does it take grapes to grow” details are shared below.

How long does it take grapes to grow?
It takes grapes three to five years to bear fruit, depending on the grape variety and growing conditions. The first year focuses on establishing strong roots, with minimal above-ground growth. By the second year, the vines develop further, and by the third year, you may start seeing some fruit. Full production typically occurs around the fourth or fifth year. Effective care, including regular pruning, proper watering, and timely fertilization, is essential to promote robust growth and maximize fruit yield.
Factors affecting grapevine growth
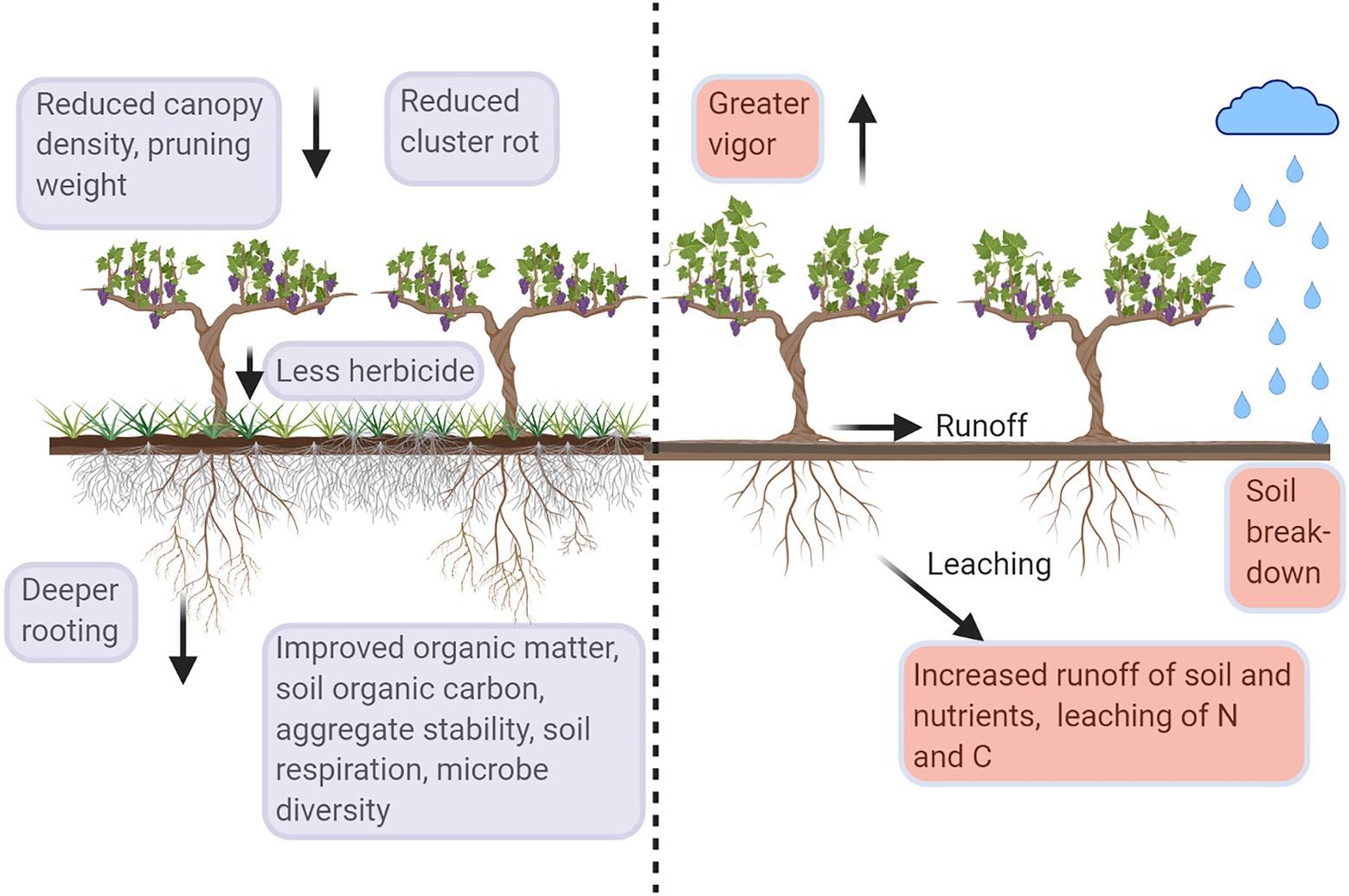
Below are some factors that affect grape growth:
Climate: The climate is pivotal for grape growth, influencing their success. Grapes thrive in temperate regions characterized by warm, dry summers and mild winters. These regions with distinct seasons provide the ideal conditions for grapevines to flourish.
Soil: The soil’s composition, pH level, and drainage profoundly impact grape development. Grapes prefer well-drained soil with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. Sandy loam soil is typically considered optimal for grape cultivation due to its balanced texture and drainage capabilities.
Nurturing the Vines: Implementing proper care practices is essential for fostering healthy grapevines. Regular pruning helps maintain vine shape and regulate fruit production. Consistent watering and appropriate fertilization promote robust growth and fruit quality.
Understanding these critical factors and adapting your care routine to suit your specific conditions can enhance grapevine health and lead to a rewarding harvest. Whether you’re tending to vines in a vast vineyard or a small backyard garden, growing grapes offers a delightful journey from vine to table.
Step-by-Step from Planting to Harvesting Grapes
Growing your own grapes can be a fulfilling and rewarding experience. From planting the grapevines to harvesting the sweet, juicy fruits, each step requires careful planning and attention. Here’s a detailed guide to take you through the process, ensuring a bountiful harvest.
Planting: Establishing Your Grapevines

The initial planting phase is crucial for establishing robust grapevines, whether you opt for grapevine cuttings or seeds. Proper planting sets the stage for healthy growth and future harvests.
From Cuttings:
- Timing: Plant grapevine cuttings in early spring when the soil is workable and before the growing season begins. Early spring provides the ideal conditions for root development, with the soil warming up and the risk of frost diminishing.
- Soil Preparation: Choose well-drained soil with a pH level between 6.0 and 6.5. If your soil is heavy or poorly drained, consider creating raised beds or amending the soil with organic matter to improve drainage. Grapevines do not tolerate waterlogged conditions, which can lead to root rot.
- Planting the Cuttings: Each cutting should measure approximately 12 inches in length. Ensure that at least two buds are above the soil line when planting. Insert the cutting into the soil at a slight angle to encourage strong root growth and anchoring. Space the cuttings about 6 to 8 feet apart to allow for proper vine expansion and air circulation, which helps prevent disease.
From Seeds:

- Starting Indoors: Start grape seeds indoors 6-8 weeks before the last expected frost date. Use seed-starting trays or small pots filled with a well-draining potting mix. Sow the seeds about 1/4 inch deep and keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Place the trays or pots in a warm, sunny location, or use a heat mat to ensure optimal germination conditions.
- Transplanting Outdoors: After the threat of frost has passed and the seedlings have developed a few sets of true leaves, transplant them outdoors into their designated growing area. Harden off the seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions over a week before planting them in the ground. Space the seedlings 6 to 8 feet apart, ensuring they have enough room to grow and mature.
These steps form the foundation for healthy vine growth, ensuring your grapevines thrive and produce abundant fruit in the seasons to come.
Growth and Care: Nurturing Your Vines
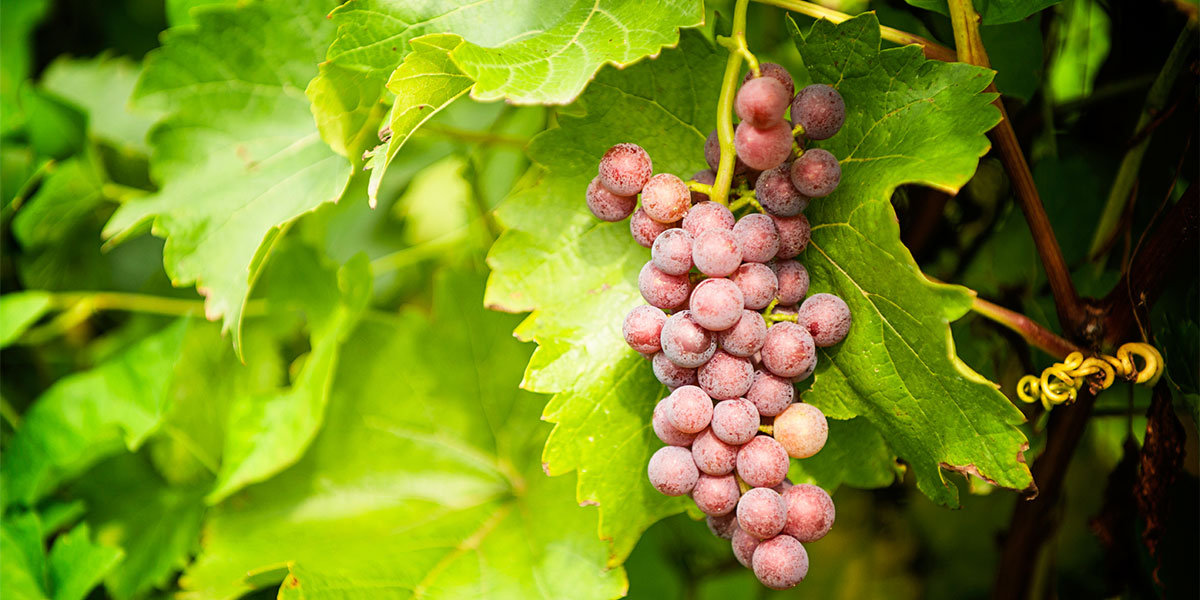

Throughout the growing season, consistent care is essential for fostering strong vines and flavorful grapes. Proper maintenance will ensure that your vines are healthy and capable of producing high-quality fruit.
Watering:
- Soil Moisture: Regular watering is crucial, especially during dry periods. Grapevines prefer soil that is consistently moist but not soggy. Deep watering encourages roots to grow deeper, making the vines more resilient to drought conditions. Water the vines early in the morning to allow excess moisture on the leaves to evaporate, reducing the risk of fungal diseases.
Fertilization:
- Nutrient Supply: Grapevines benefit from a balanced fertilizer applied at key stages of growth. Use a fertilizer with equal parts nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in early spring to encourage vigorous vine and root growth. As the growing season progresses, switch to a fertilizer with a lower nitrogen content to promote fruiting. Avoid over-fertilizing, as excessive nitrogen can lead to excessive foliage growth at the expense of fruit production.
Pruning:
- Growth Patterns: Pruning is essential for shaping the vine, controlling its size, and encouraging fruit production. During the first few years, focus on training the vine to establish a strong framework. Remove any weak, damaged, or overcrowded shoots. As the vine matures, prune in late winter or early spring to remove old wood and encourage new growth. Proper pruning improves air circulation and sunlight penetration, both of which are critical for healthy grapes.
Pest and Disease Management:
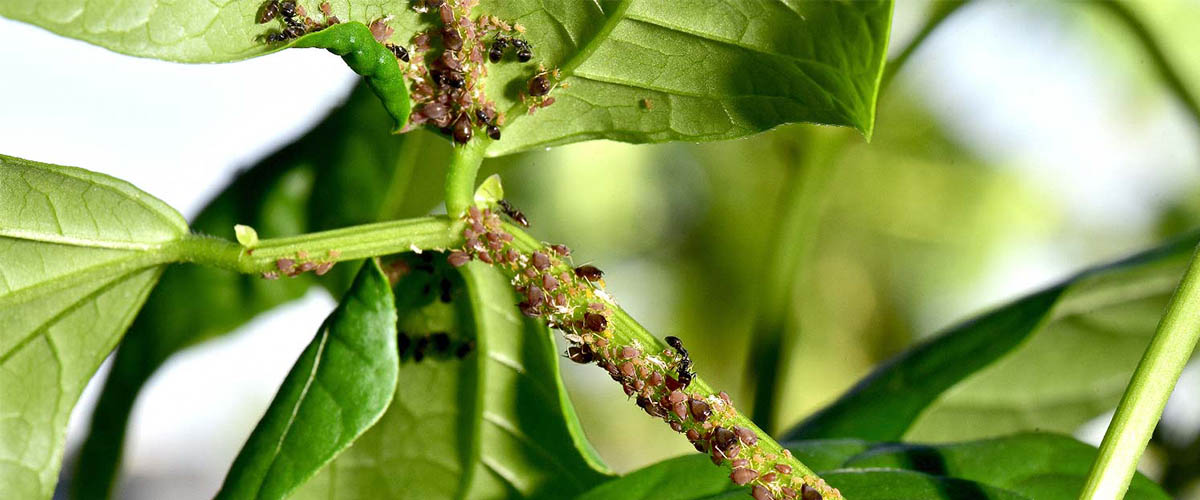

- Monitoring and Treatment: Regularly inspect your vines for signs of pests or diseases. Common grapevine pests include aphids, spider mites, and grapevine beetles, while diseases such as powdery mildew and black rot can also be problematic. Use organic or chemical controls as needed, and ensure good cultural practices, such as proper spacing and pruning, to minimize the risk of infestations.
Harvesting: Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor
Knowing when to harvest your grapes is critical for achieving the best flavor and sweetness. Grapes that are harvested at the right time will be juicy, sweet, and full of flavor.
Determining Ripeness:
- Visual Cues: Grapes are ready to be harvested when they achieve full color, are plump to the touch, and slightly soft. Different grape varieties have different ripening times, so it’s essential to know the specific characteristics of your chosen variety.
- Taste-Testing: The best way to ensure ripeness is to taste a few grapes from different clusters. Grapes do not continue to ripen after being picked, so it’s important to harvest them at their peak. The sweetness should be balanced with a slight acidity, which is characteristic of ripe grapes.
Enhancing Sweetness:
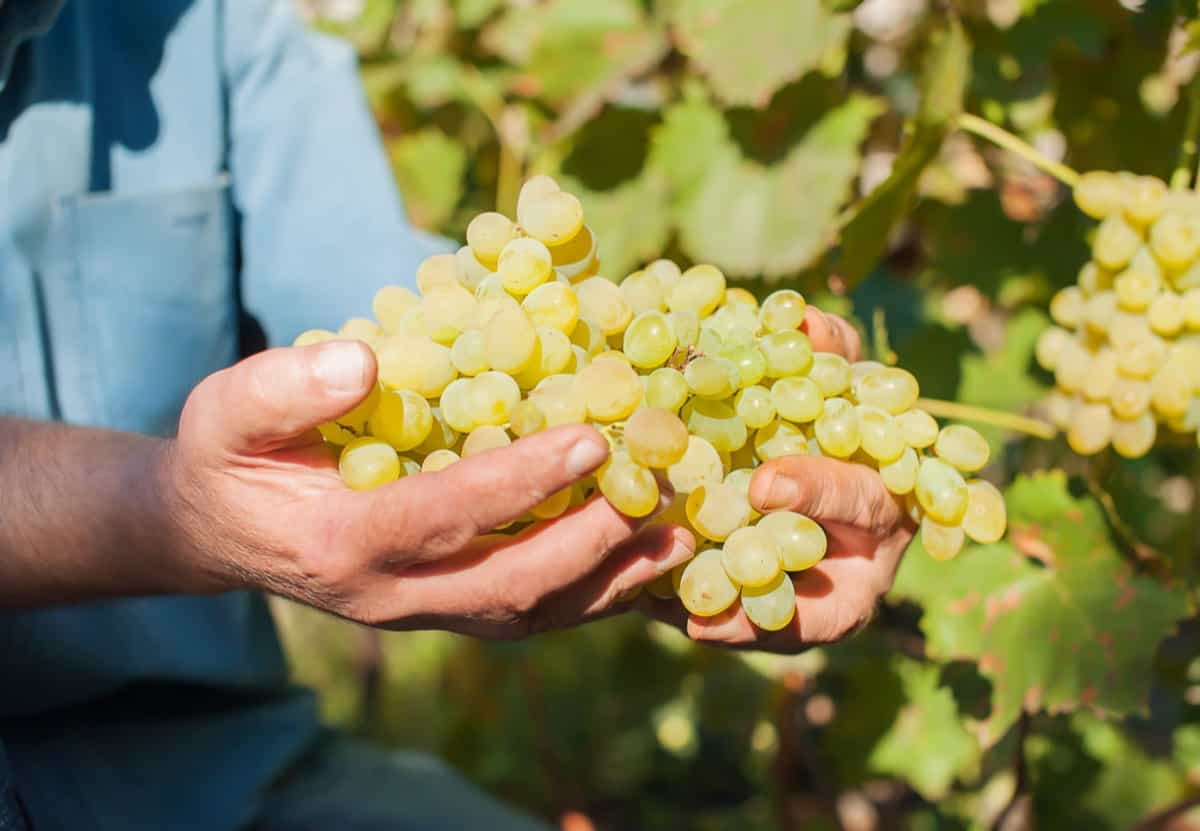

- Water Management: To enhance natural sweetness, reduce watering several weeks before harvest. This mild stress prompts the vines to concentrate sugars in the fruit. Ensure the grapes receive ample sunlight, as this is crucial for the development of sugars and flavors.
Post-Harvest Care: Preparing for the Next Season
After harvesting, it’s essential to continue caring for your grapevines to prepare them for winter dormancy and ensure vigorous growth in the coming season.
Maintaining Moisture Levels:
- Watering: Keep the soil around your grapevines adequately moist after harvesting, especially if you experience a dry autumn. This helps the vines recover from the stress of fruit production and prepare for the winter ahead.
Pruning for Winter:
- Pruning: Prune the vines after the leaves have fallen and the plants have gone dormant. Remove any old growth and shape the vines to encourage healthy growth in the spring. This is also the time to remove any diseased or damaged wood, which could harbor pests over the winter.
Winter Protection:
- Cold Protection: Depending on your climate, consider mulching around the base of the vines to protect the roots from freezing temperatures. In regions with harsh winters, you might need to protect the vines with burlap or other materials to shield them from severe cold and wind.
Measures when encountering problems related to grapes

Growing grapes is a fulfilling endeavor, yet it comes with its share of challenges. Below are some common issues grape growers encounter along with practical solutions to address them:
Pests and Diseases
Insects, birds, and diseases pose threats to grapevines. Here’s how to manage them:
- Pests: Use insect nets or organic insecticides to deter bugs.
- Birds: Protect ripening grapes with bird netting.
- Diseases: Regular pruning and proper spacing enhance air circulation, minimizing fungal disease risks.
Poor Fruit Development
If your grapes are undersized or tart, consider these remedies:
- Soil: Test soil pH and adjust with lime or sulfur as needed.
- Watering: Maintain consistent watering to support healthy fruit growth.
- Sunlight: Ensure grapevines receive ample sunlight for sweet, well-developed grapes.
Pruning Challenges
Pruning can be daunting for new grape growers. Follow this practical tip:
- Handy Hint: Prune grapevines in late winter while dormant. Remove dead or weak canes, and trim healthy canes to 8-10 buds to encourage vigorous spring growth.
Climate and Weather Concerns
Harsh weather conditions can impact grapevine health. Here’s how to mitigate their effects:
- Frost: Use frost blankets or wind machines during cold spells to protect vines.
- Heat: Shield vines from excessive heat using shade cloth.
By understanding these common challenges and implementing effective solutions, you can ensure a successful grape-growing season. Happy gardening!
Conclusion
Knowing how long does it take grapes to grow is essential for planning and cultivating a successful vineyard or garden. Typically, grapevines reach full maturity and produce a substantial harvest in about two to three years. By providing the right conditions and care during each growth stage, you can ensure your grapevines thrive and yield a bountiful harvest for years to come.

Related articles
Top 5 Spring Tree Pests: Identifying and Managing Common Threats
How to Grow Virginia Creeper: A Complete Guide
How to care for cyclamen from the expert
Detailed instructions: How to care for propagated plants
Understanding tree diseases: Identification, prevention, and treatment
Detailed instructions: How to care for fruit trees
Detailed instructions how to grow winter vegetables
How to propagate an aloe plant: a detailed guide to the methods